Ocular Refraction Neurology Teachmephysiology
Accommodation of nerve Accommodation of nerve (Science: anatomy, nerve) The property of a nerve by which it adjusts to a slowly increasing strength of stimulus, so that its threshold of excitation is greater than it would be were the stimulus strength to have risen more rapidly. Last updated on July 21st, 2021 You will also like. Sensory Systems
Snapshots of Life Wired for Nerve Regeneration NIH Director's Blog
When a current is passed into an excitable tissue V is raised at the cathode, lowered at the anode: if V is raised enough, a state of instability is reached and "excitation" occurs. In a recent preliminary treatment of this subject (Hill, 1935, b) the name "cathode potential" was used.
nerve innervations of muscles
The accommodation reflex is the visual response for focusing on near objects. It also has the name of the accommodation-convergence reflex or the near reflex. It is synkinesis which consists of the of both eyes, contraction of the ciliary muscle resulting in a change of lens shape (.

13.2 Ganglia and Nerves Anatomy & Physiology
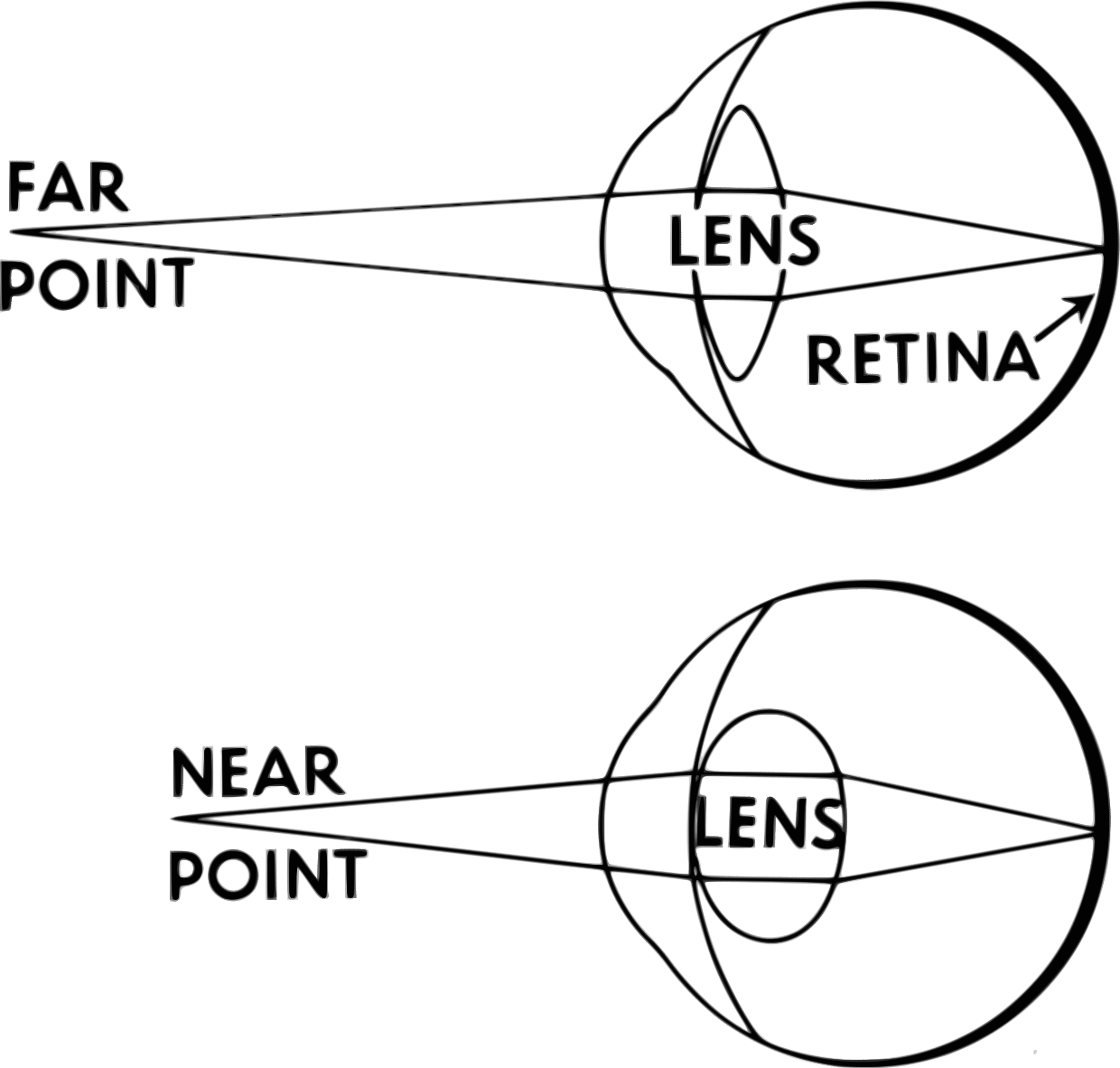
The human eye can see any object placed at a variable distance from it by altering its structure (by altering the anterior lens surface). This phenomenon is called accommodation.[1] Accommodative dysfunction is a common vision disorder among the pediatric population with or without visual disturbance and binocular dysfunction. Accommodative dysfunction is either accommodative insufficiency or.

Sensory and Motor Pathways in the Central Nervous System Nervous system, Brain diagram
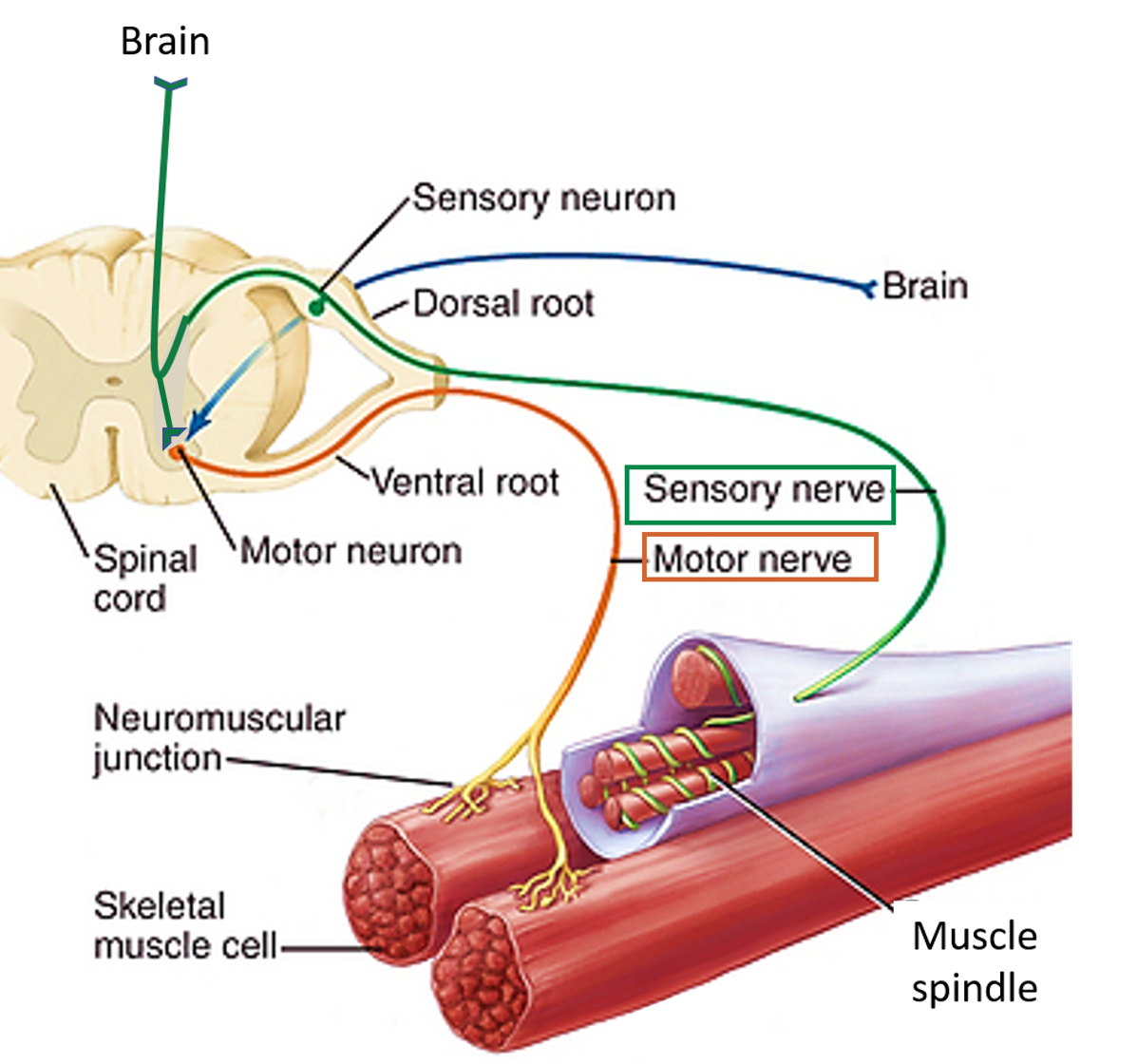
The physiology behind a "normal" pupillary constriction is a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Parasympathetic innervation leads to pupillary constriction. A circular muscle called the sphincter pupillae accomplishes this task. The fibers of the sphincter pupillae encompass the pupil.

Auditory Nerve A section of the auditory nerve in a young … Flickr
Abstract. The accommodative effects of alpha- and beta-adrenergic stimulation were investigated in human subjects by measuring changes in the response ACA ratio and in the response accommodative amplitude as a result of instilling hydroxyamphetamine hydrobromide and phenylephrine hydrochloride. Statistically significant increases in the ACA.

Reflex Special Sense Physiology YouTube
Semantic Scholar extracted view of "THE BREAKDOWN OF ACCOMMODATIONNERVE AS MODEL SENSE-ORGAN" by C. Bernhard et al.
New Human Physiology Ch 3
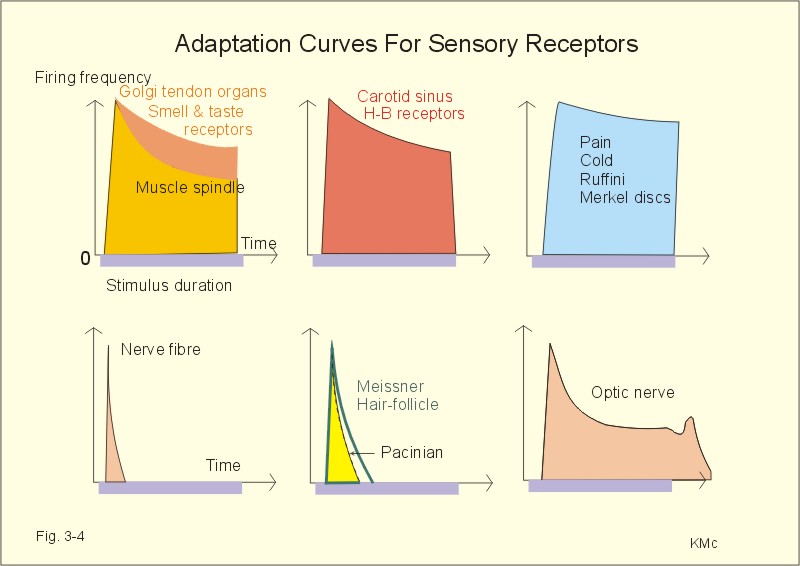
The term "accommodation" is taken to embrace both the processes that oppose the increase in axonal excitability caused by long-lasting, subthreshold depolarizing currents and also the processes of adaptation that limit repetitive firing to a maintained subthreshold current.

Anatomy Of The Visual System ANATOMY
Chapter 50 Neurology: Anatomy & Physiology Saltatory conduction → ↑ speed of propagation Gray matter: CNS regions containing nerve cell bodies, unmyelinated axons White matter: CNS regions containing myelinated axons Structural and functional classification Unipolar neurons One process, divides into two branches Mostly function in PNS as first-order sensory neurons; conduct impulses.

Anatomy of the reflex YouTube
Archive of all online content. January 1938
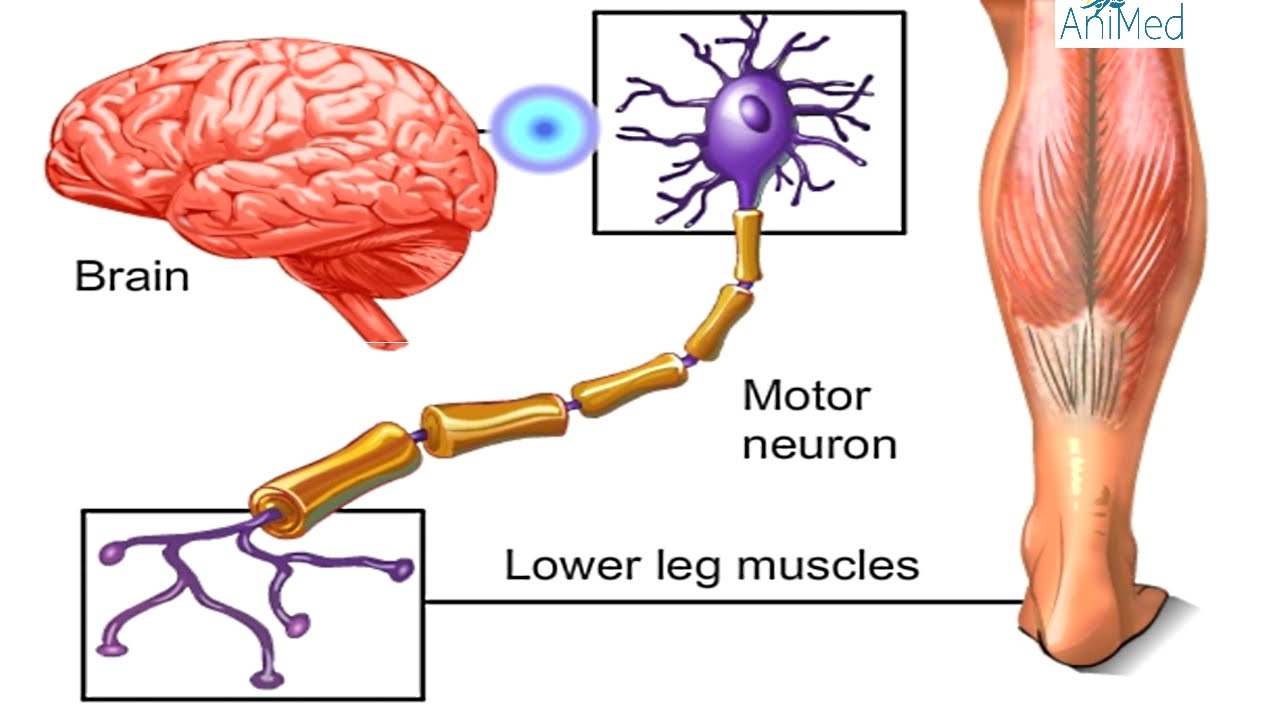
Which Neuron Transmits Signals From The Pns To The Central Nervous System? The 9 Latest Answer
The accommodation reflex (or accommodation-convergence reflex) is a reflex action of the eye, in response to focusing on a near object, then looking at a distant object (and vice versa), comprising coordinated changes in vergence, lens shape ( accommodation) and pupil size.

Neuropathy, Nerve Pain and Social Security Disability Patient Talk
Schacher theory of accommodation (2006) - This theory states that when the lens is in focus, there is increased tension on the lens through the equatorial zonular fibers and when there is contraction of the ciliary muscle, the zonular fibers located equatorially increase their tensile strength.

There are multiple types of nerves that innervate the brain. Some carry sensory inputs from the
Accommodation for Near Vision The accommodation reflex (or near response) is a three-part reflex that brings near objects into focus through lens thickening, pupillary constriction, and inward rotation of the eyes—eye convergence.

This diagram shows the connections between the different nerves and pathways in the eyes. A hand
Accommodation refers to dynamic changes in the refractive power of the lens, which is achieved by modifying the shape of the lens. The shape of the lens is controlled by two opposing forces: The internal elasticity of the lens, which tends to keep the lens rounded up. A more curved lens refracts light to a greater degree.

The Vestibular System and EOMs Part 2 Anatomie und physiologie
Archive of all online content. January 1938 January 2020. 1930s; 1940s; 1950s; 1960s; 1970s; 1980s; 1990s; 2000s; 2010s; 2020s

Simplified nerve physiology and the clinical applications YouTube
Neural accommodation or neuronal accommodation occurs when a neuron or muscle cell is depolarised by slowly rising current ( ramp depolarisation) in vitro. [1] [2] The Hodgkin-Huxley model also shows accommodation. [3]