Delirium vs Dementia National Hospice Cooperative
Nurses play a pivotal role in the maintain of patients with confusion and altered mentally status, and their nursing care set should be individualized to the patient's demand and circumstances. Which plan should include strategies since assessing and check the patient's mental position, providing a unhurt and supportive environment, managing any behavioral disturbances, furthermore.
Delirium Nursing Diagnosis and Care Management Nurseslabs
This plan should include strategies for assessing and monitoring the patient's mental status, providing a safe and supportive environment, managing any behavioral disturbances, and communicating with the patient's healthcare team and family members. Use this nursing diagnosis guide to help you create an acute confusion nursing care plan.

Delirium Medicine
Delirium, also known as an acute confessional state, is a clinical syndrome that usually develops in the elderly. It is characterized by an alteration of attention, consciousness, and cognition, with a reduced ability to focus, sustain or shift attention. It develops over a short period of time and fluctuates during the day. The clinical presentation can vary, usually demonstrating psychomotor.
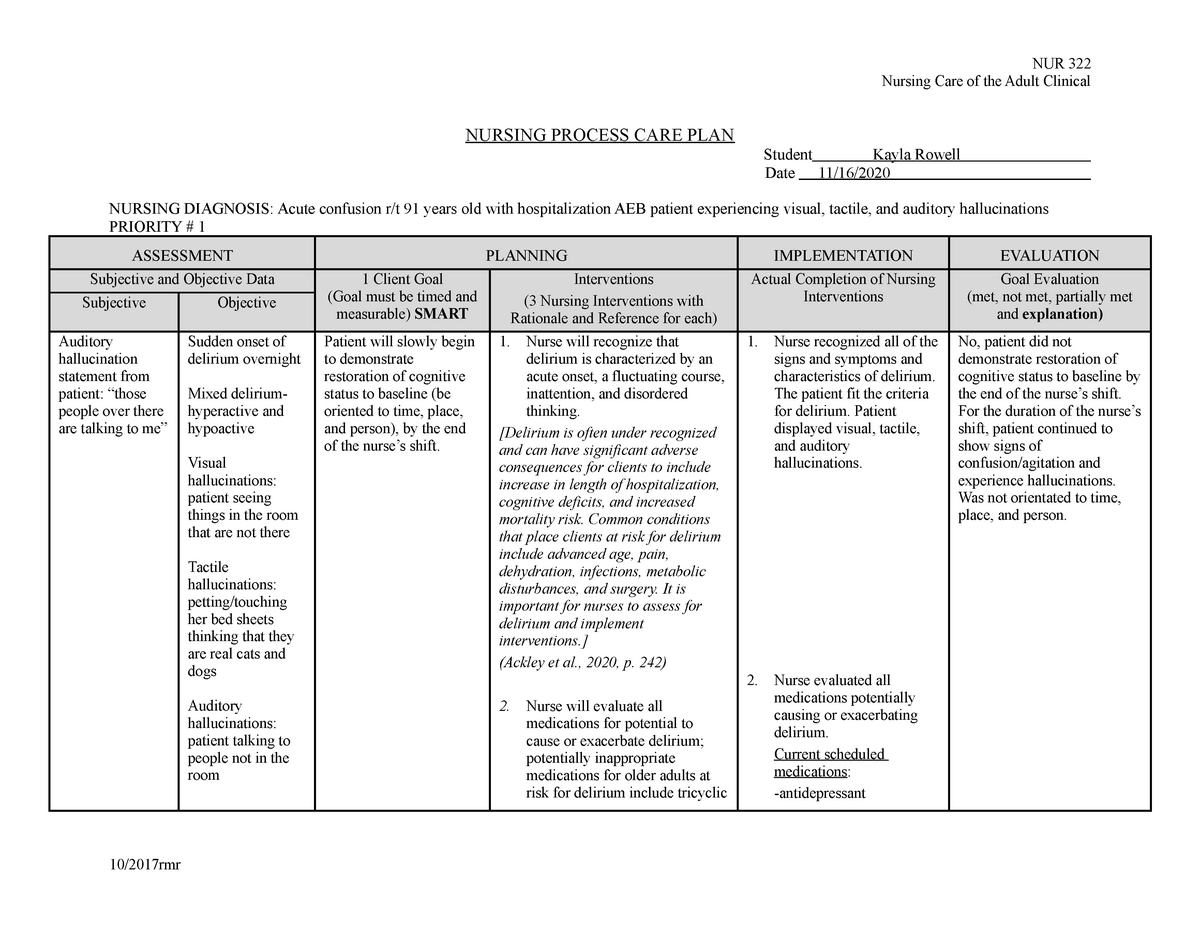
Medsurg Care Plan Nursing Care of the Adult Clinical NURSING PROCESS CARE PLAN Student Kayla
Introduction to Nursing Care Plan for Delirium. Delirium is a common, serious and challenging condition seen in hospital settings. It is an acute brain disorder characterized by a range of symptoms including confusion, disorientation, attention deficits, delusions and hallucinations.
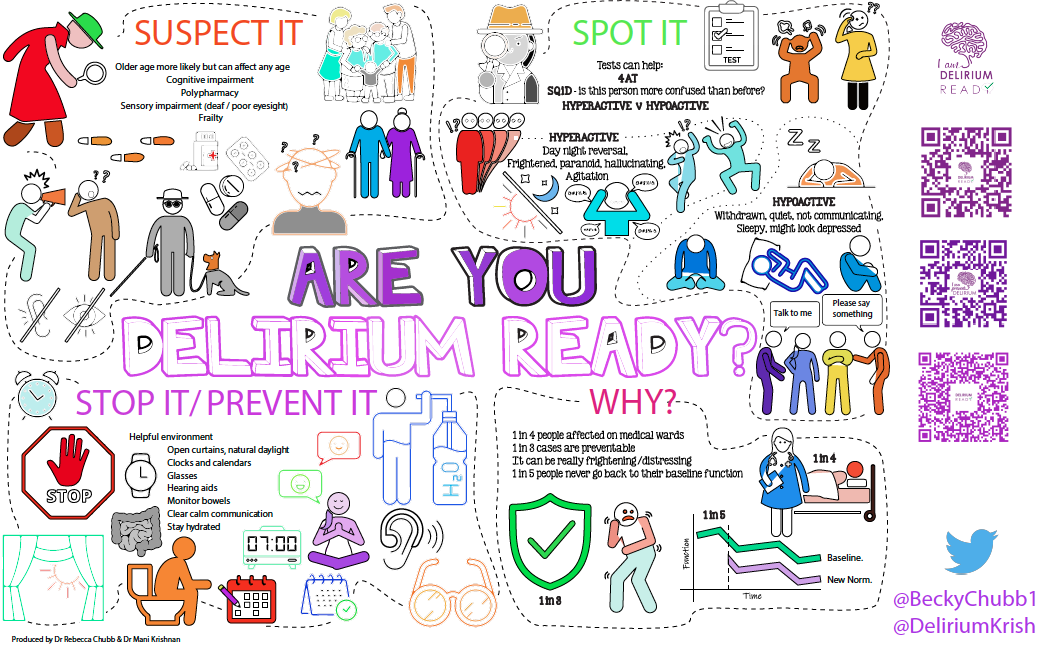
Delirium Resources
Nursing Care Planning and Goals. The major nursing care plan goals for delirium are: Client will maintain agitation at a manageable level so as not to become violent. Client will not harm self or others. Nursing Interventions. Nursing interventions for patients with delirium include the following: Assess the level of anxiety.

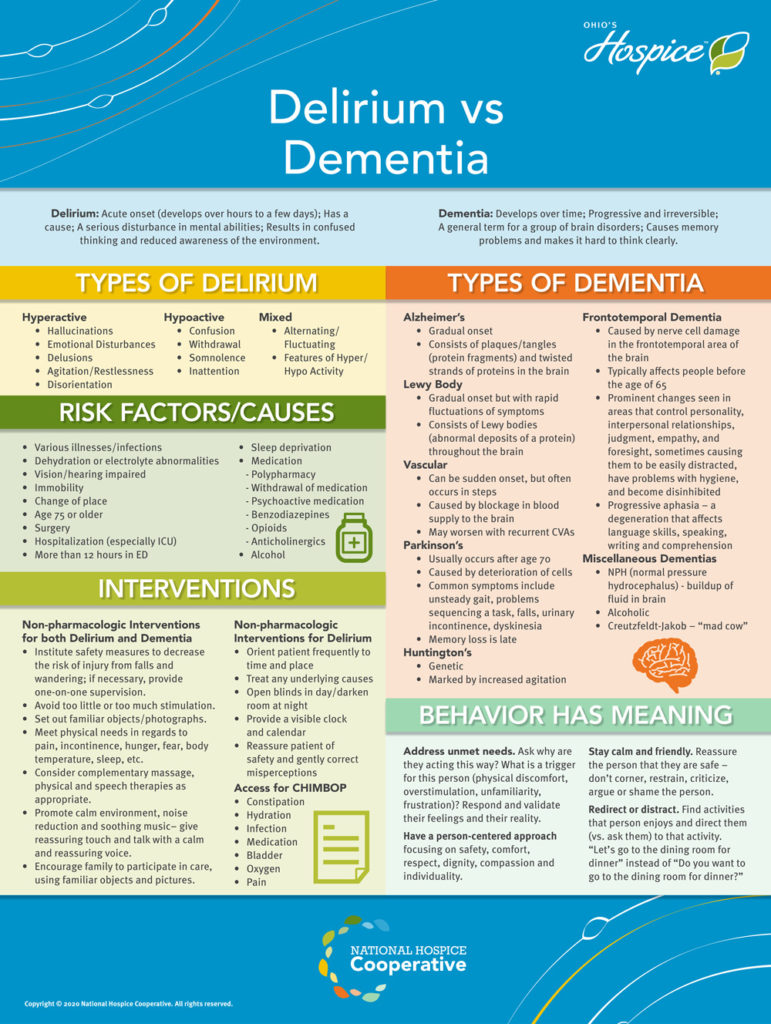
The Difference Between Delirium and Dementia
Delirium is a medical emergency. To intervene appropriately and prevent complications, nurses must know delirium risk factors, fre-quently assess patients for signs and symptoms of delirium, and advocate for treatment to improve patient-care outcomes and quality of life. REFERENCES 1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic

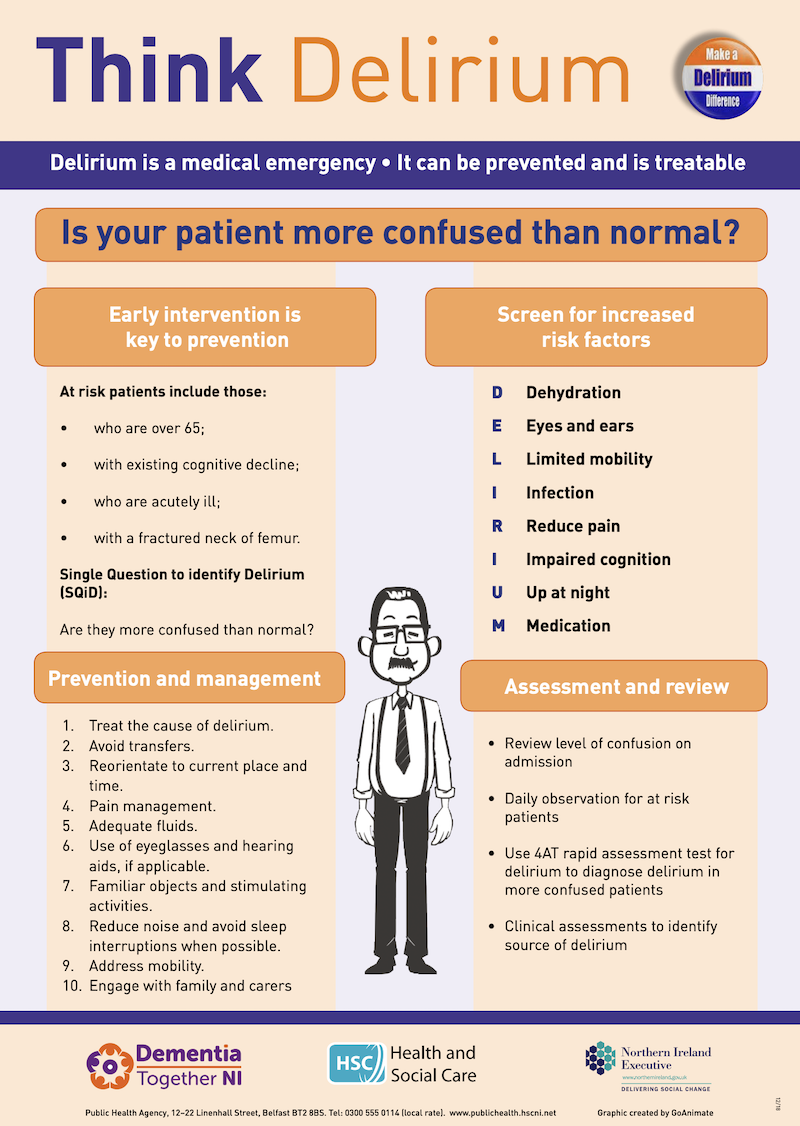
Delirium Ausmed Course 0.5 CPD Hours
Delirium is an acute, transient, usually reversible neuropsychiatric syndrome, seen in medical-surgical set-ups. It is considered to be a serious problem in acute care settings. Although delirium is encountered in all age groups, elderly are considered to be a high-risk group for development of delirium. It basically reflects decompensation of.

Delirium Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis and Interventions
Delirium is defined as an acute, fluctuating syndrome of altered attention, awareness, and cognition. It is common in older persons in the hospital and long-term care facilities and may indicate a.

Nursing Care Plan on Delirium ll Mental health and psychiatric nursing YouTube
Delirium is an acute disturbance of mental status and cognition with and acute onset of hours or days. It is often related up dehydration, infection, medications… Delirium be an acute disrupt of mental level and cognition with an urgent onset of clock or life.
PPT Delirium Patient Story PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1895047
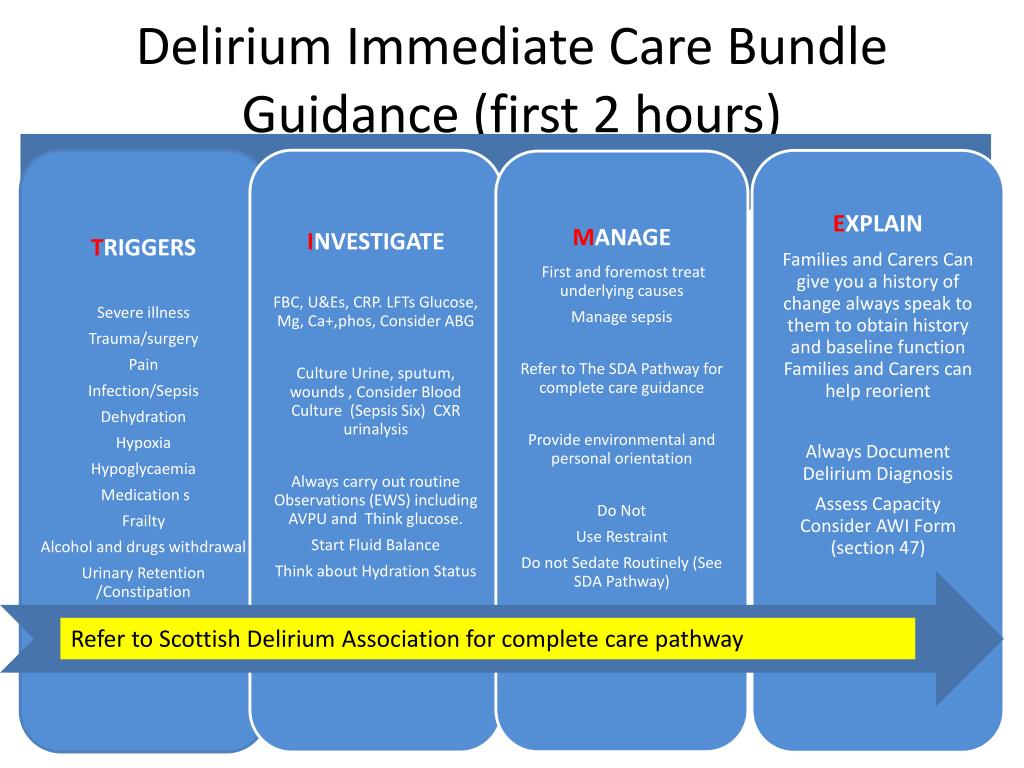
Delirium Prevention and Management Care Plan Guidance based on NICE Clinical Guideline 103 . Patient name: _____ Unit no: _____ Severe illness . For each individual patient, the clinical factors contributing to the risk of, or the episode of, delirium will vary. The same clinical factors act as risk factors which you can act on to prevent an.

Nursing strategies for managing delirium Nurse, Gerontology nursing, Geriatric nursing
A. Delirium is a common syndrome in hospitalized older adults and is associated with increased mortality, hospital costs, and long-term cognitive and functional impairment. B. Delirium may be prevented or diminished with the recognition of high-risk patients and the implementation of a standardized multicomponent delirium-reduction protocol.

Delirium Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Care Plan
Critical Care Medicine, 41(1), 263-306. Doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182783b72. The article updates and includes evidence-based guidelines and recommendations for healthcare professionals for the prevention and management of delirium in the critical care setting. This was done by an interdisciplinary task force of twenty individuals over a six year.

Exploring how registered nurses assess and identify delirium in older persons in the hospital
This allows the health care provider to monitor the patient, begin treatment of the underlying problem, and develop a long-term care plan with the patient and/or family. Supportive care — The goal of supportive care is to maintain the patient's health, prevent additional complications, and avoid those factors that can aggravate delirium. This.

Delirium Nursing Strategies
Delirium Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan. Delirium is an acute disturbance of mental status and cognition with an acute onset of hours or days. It is often related to dehydration, infection, medications, alcohol withdrawal, dementia, organ failure, severe pain, or the dying process. Hyperactive. Patients are often restless, anxious, have rapid.
Delirium Sunnybrook Hospital
Supportive care. Care for older people with delirium involves special hospital care with careful attention to medical, environmental, and social situations. People with delirium are particularly vulnerable to medical complications such as falls, dehydration or malnutrition, pressure ulcers, joint stiffness, constipation, or wetting the bed.

The delirium care pathway (DCP) flow diagram. See text for description... Download Scientific
A quick guide for care home managers. Think delirium! Delirium is a sudden change in a person's mental state. It is a serious condition that is sometimes mistaken for dementia or, more rarely, depression.. Assess and plan. Factors that make delirium more likely are listed below, with steps to help reduce the risk. Cognitive impairment or.